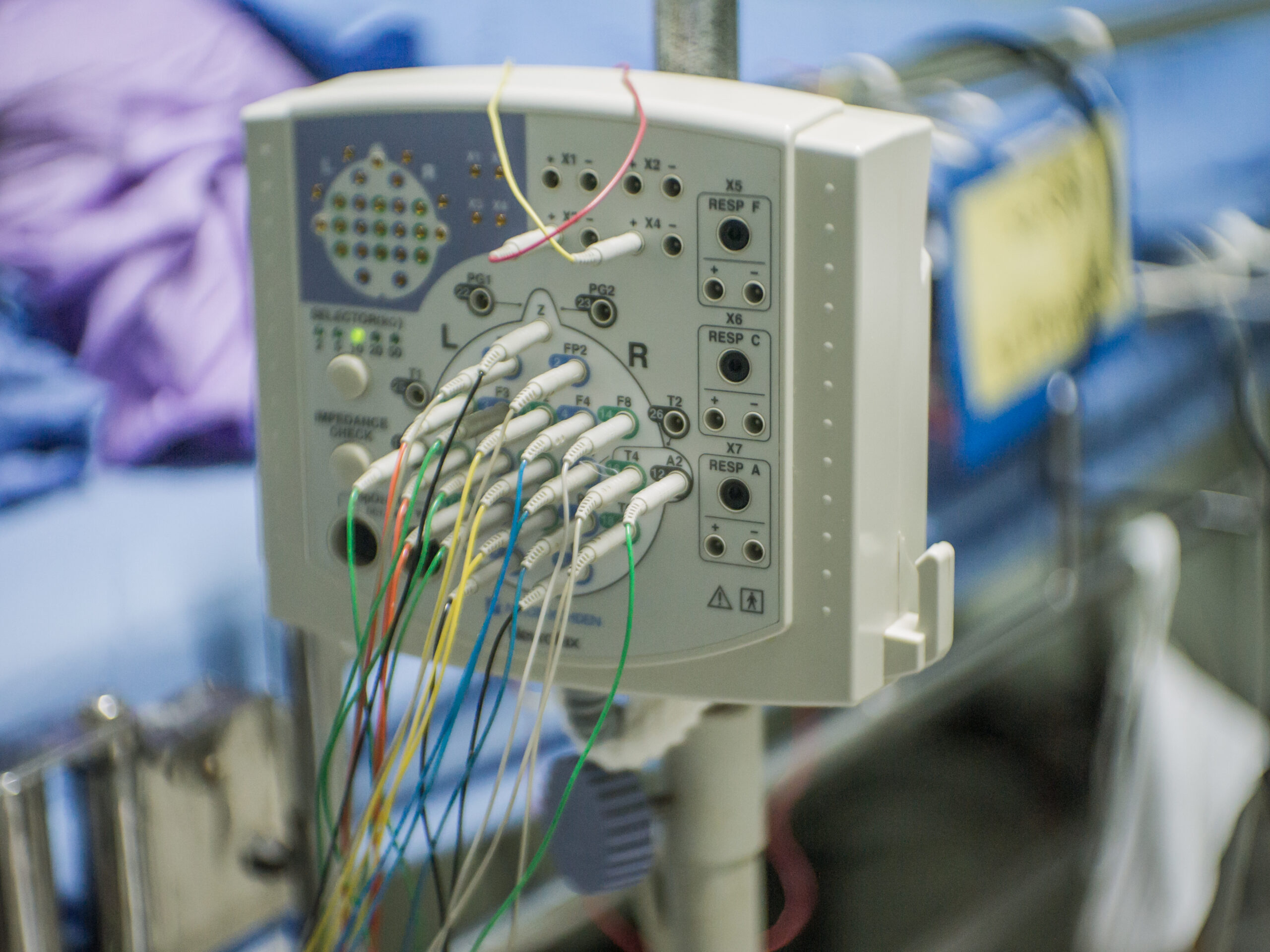
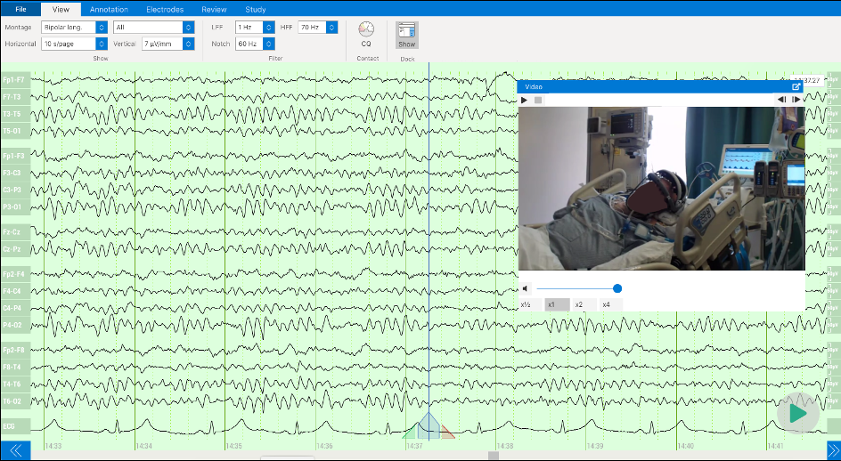
EEG in the ICU offers unparalleled insight into the neurological status of patients. Facilitating ease of use is a cornerstone of making sure this vital marker is not overlooked.
In the fast-paced world of healthcare, where every moment can be crucial, monitoring a patient’s neurological status is often overlooked in emergency situations. However, research findings suggest that integrating EEG (electroencephalogram) monitoring into critical healthcare settings can have profound benefits, especially for patients requiring prompt neurological evaluation
EEG in the ICU
In Intensive Care Units (ICUs), where vigilant monitoring of patient health is crucial, traditional focus areas like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are routinely scrutinized. EEG monitoring in the ICU is often used for continuous, long-term monitoring of brain activity in critically ill patients. It’s particularly crucial for detecting non-convulsive seizures, assessing the depth of coma, and monitoring for changes in brain function in patients with severe brain injuries, stroke, or those at risk of neurological deterioration. The second biggest neurological emergency after stroke is Status Epilepticus, defined as “A seizure that lasts longer than 5 minutes, or having more than 1 seizure within a 5 minute period, without returning to a normal level of consciousness between episodes is called status epilepticus. This is a medical emergency that may lead to permanent brain damage or death.” For more info see here.
Unfortunately, the monitoring of brain activity doesn’t receive the same level of attention. This is despite various critical care and neurophysiology societies providing guidelines for EEG indications in the ICU. This oversight can be critical, especially since conditions like non-convulsive seizures can go unnoticed without proper EEG monitoring. Research indicates that timely access to EEG monitoring is vital for effective patient management, and any delays can have significant impacts, not just on patient outcomes but also on hospital operational efficiencies.
Challenges in the ICU
The Neurocritical Care Society guidelines advise that patients suspected of having Nonconvulsive Status Epilepticus in ICU should get an EEG test within 15 to 60 minutes.
The primary challenge in intensive care unit is the lack of specialized EEG or neurology staff, which can lead to delays in detecting and treating critical neurological conditions.
The complexity of traditional EEG equipment also poses a challenge, as it requires time and expertise to set up and interpret. This can be problematic in the ICU, where rapid response and treatment are often necessary. Non-convulsive seizures, for instance, are common in critically ill patients but can be difficult to detect without proper EEG monitoring. Studies suggest that delays in EEG access can extend hospital stays, emphasizing the need for more accessible EEG solutions.
A pressing challenge is accurately assessing brain activity, especially in post-cardiac arrest patients. While vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure are meticulously monitored, determining the status of the brain remains a complex task. In the case of patients who have experienced cardiac arrest, assessing neurological function without EEG is nearly impossible. These patients may exhibit varying degrees of consciousness to comatose, making it difficult to discern subtle neurological changes. Traditional methods often fall short in providing a comprehensive understanding of brain activity, highlighting the critical need for accessible and efficient EEG monitoring solutions like that of Zeto EEG.
Additionally, a key factor with EEGs in the ICU is timing. Even large academic hospitals offering 24/7 coverage of conventional EEG have reported a median delay of four hours to initiate EEG monitoring. Additionally, the process of applying EEG leads on a patient’s head using a traditional EEG system further contributes to these time delays, impacting the speed at which critical monitoring can begin.
Another major barrier to effectively leveraging EEG in the ICU is the lack of bedside diagnostic capabilities. Live, remote interpretation by a physician is simply a must, to ensure that an expert is on hand to diagnose and treat in a timely manner. Live video and continuous monitoring by remote techs would provide the highest quality of care in these situations.
Solving the Problem of EEG in the ICU, With Zeto
Zeto’s EEG system is designed to meet the unique demands of the ICU. Zeto’s EEG headset is full-montage with single-use electrodes. Additionally, it is wireless and portable, eliminating the need to wait for a cart to be brought into the ICU. It offers a rapid setup and user-friendly interface, making it accessible to healthcare professionals who may not have specialized training in neurology. This ease of use is a significant advantage in the ICU, where time and accessibility are crucial. The system’s design allows for quick application and immediate monitoring, facilitating faster response times in critical situations.
With Zeto EEG, bedside diagnostics becomes possible, with remote, continuous real-time monitoring by EEG techs and interpretation services from neurologists available, Zeto EEG facilitates high quality care.
The Zeto EEG system also addresses the challenge of interference from other medical devices in the ICU with its state-of-the-art active electrode technology, noise shielding and noise cancellation technology.
Benefits and Features of Zeto EEG in the ICU
Zeto’s EEG system offers several key features that make it particularly suited for the ICU environment:
- Bedside Diagnostics with Accurate Seizure Detection: Timely detection of non-convulsive seizures is crucial for patient care. Zeto’s system integrates FDA-cleared seizure detection with notifications, ensuring that these critical events are not missed. Learn more about seizure detection tool here.
- Live video through the cloud: Zeto is compatible with any integrated or USB-enabled camera. The cloud’s live/remote capabilities allow for real-time observation of patients during suspected seizures.
- The portability and ease of setup of the Zeto system mean it can be quickly deployed and used across different patients, adapting to the dynamic and fluid nature of the ICU.
- Special response service for Stat EEG (Status Epilepticus): If you do not have neurologists available to interpret your EEGs, you can easily order this service through our cloud platform.
- Remote monitoring by EEG techs
- Remote monitoring by board certified neurologists
EEG in the ED
In Emergency Departments (EDs), EEG is typically used for acute diagnostics rather than long-term monitoring. It may be employed to differentiate between epileptic seizures and other conditions (like syncope, psychogenic nonepileptic seizures, or coma) or to confirm status epilepticus when a seizure is not visible.
While ED staff excel at providing immediate care for life-threatening conditions, brain activity monitoring is not always a routine part of the process. However, research findings suggest that
integrating EEG monitoring into the ED’s toolkit can have far-reaching benefits,
especially for patients with conditions requiring prompt neurological evaluation.
Challenges with EEG in the ED
One of the primary challenges in the ED is the limited time available for comprehensive assessments. Research shows that this constraint can lead to missed opportunities for detecting critical neurological conditions, such as non-convulsive seizures or non-convulsive status epilepticus. Patients in the ED may not exhibit obvious seizure symptoms, even after injuries that would seem to typically present them, such as traumatic brain injury, making EEG monitoring even more essential for timely diagnosis.
Furthermore, EDs typically lack specialized neurology staff, and the complexity of traditional EEG equipment can hinder its utility in this fast-paced environment. The need for quick setup and interpretation is evident, given that delays in EEG access can impact patient outcomes. Numerous research findings emphasize the critical role of EEG monitoring in emergency department (ED) settings, highlighting the potential risks associated with overlooking neurological conditions.
Zeto’s Solution for the ED
Zeto’s EEG system is tailored to address the unique challenges of the ED. It offers a streamlined setup process that can be quickly implemented by ED staff, who may not have specialized neurology training. This ease of use is vital in an environment where every minute counts, and rapid response can be a matter of life and death.
The Zeto EEG system also features advanced seizure detection capabilities, aligning with the need for timely diagnosis in the ED. Seizures will be automatically detected and marked in the EEG for review. Near real-time detection notifies medical staff about patients with ongoing clinical seizures. This capability is particularly valuable in the ED, where rapid neurological assessments are essential.
Benefits and Features of Zeto in the ED
Zeto’s EEG system offers several key features that make it a valuable tool in the ED:
- Quick Setup: In the high-pressure environment of the ED, simplicity is paramount. Zeto’s full-montage headset is designed for quick deployment without any preparation needed, enabling ED staff to initiate EEG monitoring rapidly (the average time is 5 minutes).
- Ease of Use: If EEG techs are not available, any ED nurse or medical assistant can be trained to do EEG with Zeto. Wireless and portable, Zeto headset enables straightforward setup at a patient’s bedside, facilitating immediate EEG monitoring using a laptop.
- Video EEG via cloud: Zeto is compatible with any integrated or USB-enabled camera and the cloud’s live/remote capabilities allow for real-time observation of patients during suspected seizures.
- Single-use disposable electrodes: Zeto’s electrodes are dry and soft, and designed for convenience and patient comfort, requiring no paste, gel, or cleanup.
- Fast turnaround time: Zeto’s EEG system facilitates a swift turnaround time, allowing for instant EEG monitoring and rapid decision-making, essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment in emergency scenarios.
- Remote EEG Reading: Zeto offers a Remote EEG Reading Service accessible through the Zeto Cloud Platform. A team of remote, certified, and specially trained adult and pediatric epileptologists provides real-time or retrospective EEG interpretation across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico.
- Remote EEG monitoring: Zeto provides real-time remote video EEG monitoring by registered EEG technologists (R.EEG.T) when such personnel are unavailable on-site. This service is available in real time upon request with a 30-minute notice 24/7/365, at no extra charge during nights, weekends, or holidays.
- These features collectively enhance the ED’s ability to provide comprehensive care, including neurological assessments, to patients who may present with complex medical conditions. The Zeto EEG system’s adaptability and efficiency align with the dynamic nature of the ED, where quick assessments and decision-making are critical.
Contact us to learn more and to schedule a demo or consultation. You’ll discover how our technology can advance your hospital’s neurodiagnostic capabilities. Join us in leading the change towards better, more efficient patient care.