Advancements in seizure detection technology provide essential tools for precise diagnosis and management of neurological conditions. Zeto integrated a full suite of FDA cleared EEG Trending, Seizure, and Spike Detection tools from encevis* into the Zeto cloud platform for quick and seamless assessment of full montage EEG signals in the ICU, inpatient and outpatient environment providing more capability vs. competitors.
Zeto’s cutting-edge EEG solutions are designed to enhance patient care and streamline clinical processes. Encevis is powered by the AIT Austrian Institute of Technology, a renowned research and technology organization in Europe, and their EEG analysis software is widely utilized and peer reviewed by physicians across the world.
Zeto Offers:
| Zeto EEG Setup Time | < 5 minutes after only 2 hours training |
| Full Montage EEG | 19 channels, non-inferior to traditional EEG[3] |
| Time to Seizure Detection | < 2-3 minutes |
| Seizure Detection [4] | High sensitivity at low false alarm rates. Proven by three independent clinical trials to get a reliable system that will provide a detailed overview of seizures and suspicious EEG activity. [2, 4] |
| Spike Detection [5] | Detects spikes and sharp waves with a very high sensitivity combined with a high specificity. Sensitivity of 89% was measured together with a specificity of 70%.[1, 5] |
| EEG Trending [4,5,6] | Graphically visualizes the results of several hours of EEG to allow a quick assessment of the state of the patient. The software works in near real time and allows reading of trends in the functional state of the patient’s brain in one glimpse.[1] |
| Amplitude-Integrated EEG [6] | General amplitude and symmetry can be read easily in the quantitative EEG panels and in the amplitude-integrated EEG. This allows a quick assessment of the state and trend of the patient |
| Burst Suppression [6] | Burst suppression events and the relative amplitude attenuation including suppression time of the bursts. |
| Artifact Reduction: PureEEG [1,2] | PureEEG removes artifacts automatically. It removes artifacts such as electrode movements, muscle contractions, line noise and head movements, etc. |
| Notification Features | One-time setup enables notification templates (email or text) to be shared automatically with a select group of stakeholders (physicians, nurses, techs) when programmable seizure thresholds are exceeded. This is not a seizure alarm but a notification infrastructure that informs decision makers about the results of the Encevis seizure detection tool. |
Seizure Detection Technologies and Their Impact
EEG trending plays a pivotal role in patient assessment, allowing clinicians to view near real-time data and react swiftly to patient needs. Innovations such as amplitude-integrated EEG and burst suppression analysis provide deeper insights, while PureEEG technology effectively reduces artifacts, ensuring cleaner and more accurate readings.
Integrated EEG Trending, including Burst Suppression, Seizure Detection and Load:
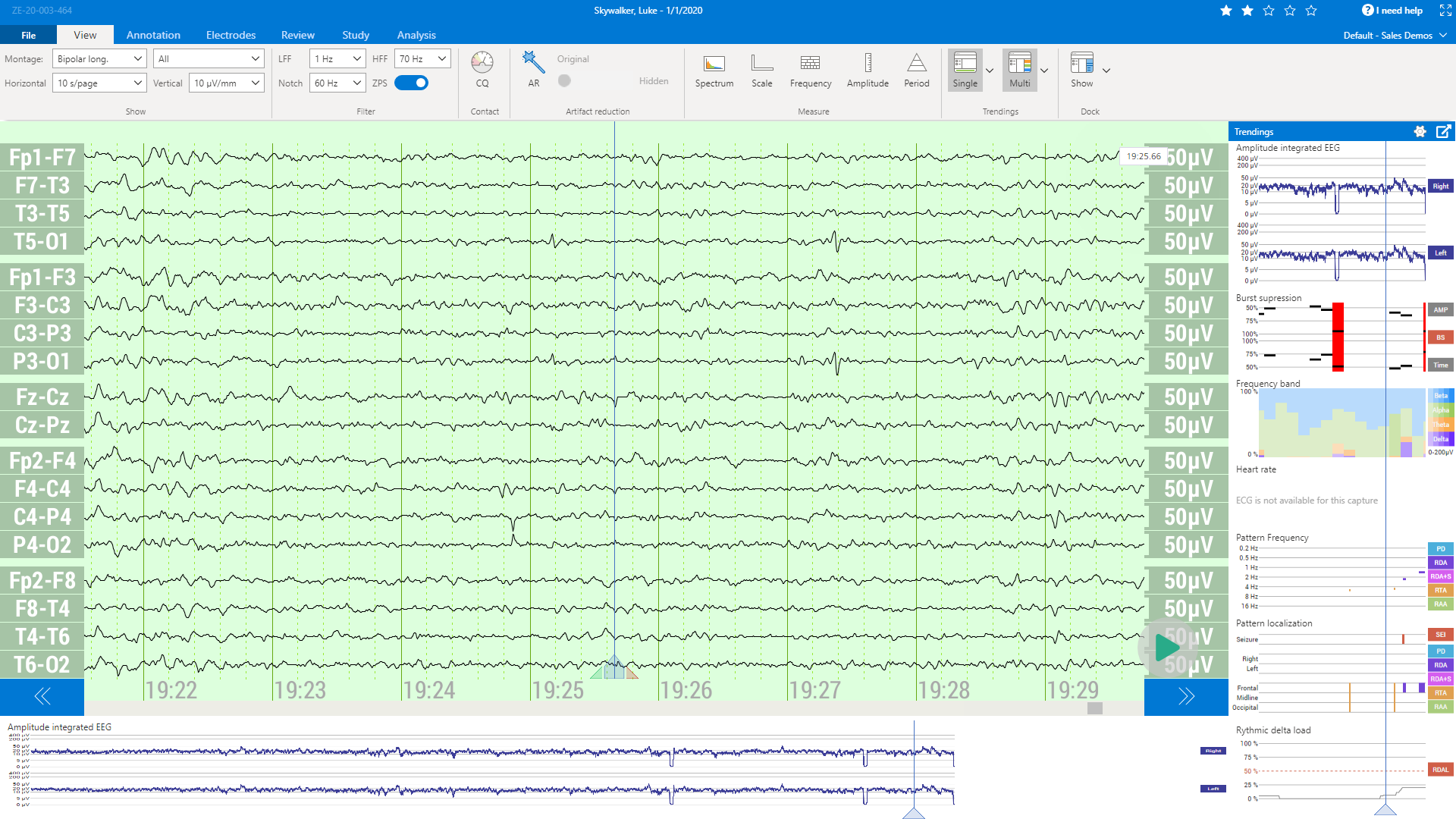
Zoom-In of the EEG Trending Panel:
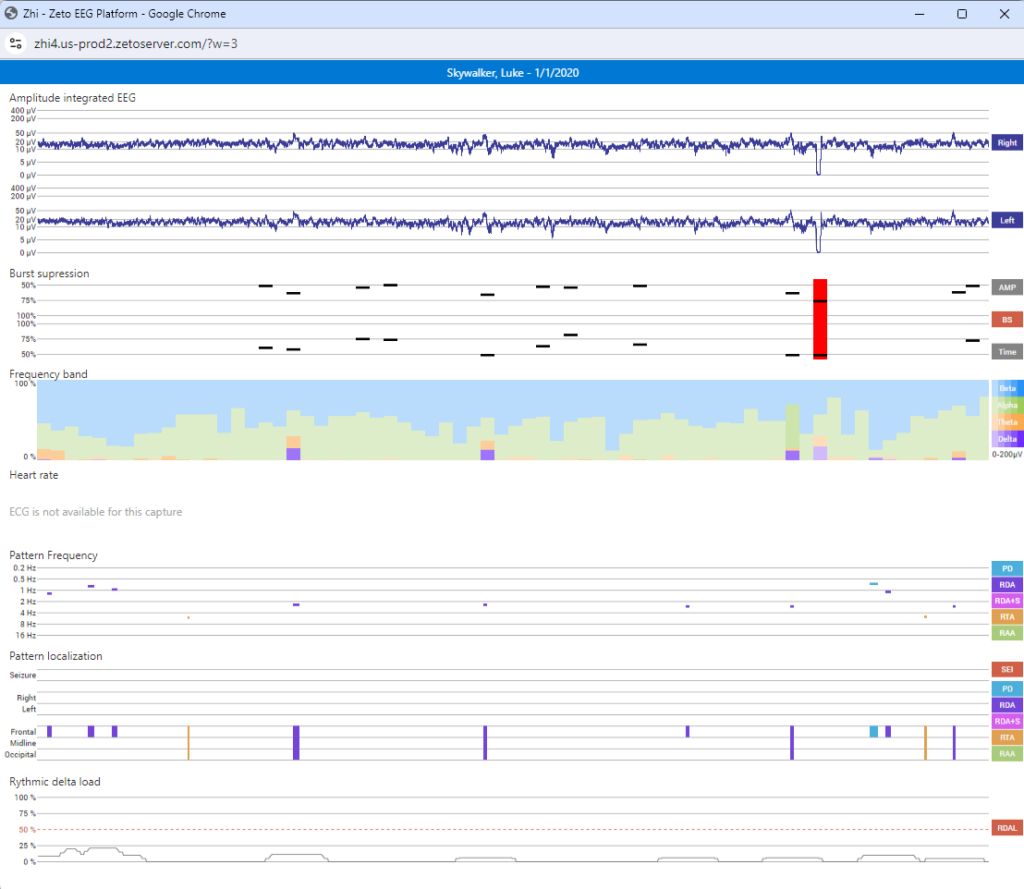
Enhancing Clinical Efficiency
The integration of seizure detection features streamlines clinical workflows and enhances communication among healthcare professionals. This is achieved through effective notifications that alert clinical staff about critical patient developments, improving decision-making and patient care.
Seizure Detection vs Seizure Burden
Seizure detection and seizure burden are two critical but distinct concepts in epilepsy management. Seizure detection focuses on the immediate identification and recognition of individual seizure events using technologies such as EEG monitoring systems, which can pinpoint abnormal brain activity in near real-time. This allows for timely intervention and management during an episode. On the other hand, seizure burden refers to the cumulative impact of seizures over time, encompassing the frequency, duration, and severity of the episodes. While seizure detection aims to identify seizures as they happen, seizure burden assesses the broader, ongoing effects of the condition.
Zeto offers an FDA-cleared seizure detection tool compared to competitors that only perform seizure burden.
AI-enabled Notifications for Seizure
AI-enabled notifications provide near real-time notifications enhancing timely intervention and patient management. It works by continuously analyzing EEG data in near real-time using advanced algorithms, instantly notifying healthcare providers when abnormal brain activity indicative of a seizure is detected.
| Feature | Benefit to Clinicians |
| Rapid EEG Setup | Minimizes patient discomfort and maximizes clinical efficiency |
| Full Montage EEG | Provides comprehensive brain activity analysis |
| High Sensitivity with Low False Positives | Enhances diagnostic accuracy |
| Amplitude-Integrated EEG | Simplifies interpretation of EEG data |
| Burst Suppression Analysis | Crucial for assessing severe neurological conditions |
| Artifact Reduction with PureEEG | Ensures clarity and accuracy of EEG readings |
Zeto’s advancements in EEG technology mark a significant milestone in neurological care, promising improved patient outcomes and operational efficiencies. The future of EEG monitoring looks bright, with ongoing innovations poised to further revolutionize the field.
To learn more about Zeto’s wireless, dry-electrode, full-montage EEG headset with remote monitoring and seizure detection, please contact us to schedule a chat and a demo.
*The encevis Component for Detection of Seizures and Electrographic Status Epilepticus is indicated for the detection of Seizures and Electrographic Status Epilepticus in patients greater than or equal to 18 years of age who are at risk for seizures.
References:
[1] PureEEG: Automatic EEG artifact removal for epilepsy monitoring, Hartmann, M.M., Schindler, K., Gebbink, T.A., Gritsch, G., Kluge, T., Neurophysiologie clinique/Clinical Neurophysiology, November 2014
[2] https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf17/K171720.pdf
[3] https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf17/K172735.pdf
[4] Seizure detection
- Improving staff response to seizures on the epilepsy monitoring unit with online EEG seizure detection algorithms, N. Rommens, E. Geertsema, L. Jansen Holleboom, F. Cox, G. Visser, Epilepsy & Behavior, July 2018.
- Automatic multimodal detection for long-term seizure documentation in epilepsy, F. Fürbass, S. Kampusch, E. Kaniusas, J. Koren, S. Pirker, R. Hopfengärtner, H. Stefan , T. Kluge, C. Baumgartner, Clinical Neurophysiology, August 2017.
- Prospective multi-center study of an automatic online seizure detection system for epilepsy monitoring units. F. Fürbass, P. Ossenblok, M. Hartmann, H. Perko, A. M. Skupch, G. Lindinger, L. Elezi, E. Pataraia, A. J. Colon, C. Baumgartner, and T. Kluge, Clinical Neurophysiology, vol. 126, no. 6, pp. 1124–1131, Jun. 2015.
[5] Spike detection
- Accurate identification of EEG recordings with interictal epileptiform discharges using a hybrid approach: Artificial intelligence supervised by human experts, M. Aykut Kural, J. Jing, F. Fürbass, H. Perko, E. Qerama, B. Johnsen, S. Fuchs, B. Westover, S. Beniczky, Epilepsia, February 2022.
- Activation patterns of interictal epileptiform discharges in relation to sleep and seizures: An artificial intelligence driven data analysis, F. Fürbass, J. Koren, M. Hartmann, G. Brandmayr, S. Hafner, C. Baumgartner, Clinical Neurophysiology, July 2021.
- An artificial intelligence-based EEG algorithm for detection of epileptiform EEG discharges: Validation against the diagnostic gold standard. F. Fürbass, M. A. Kural, G. Gritsch, M. Hartmann, T. Kluge, S. Beniczky, Clinical Neurophysiology, April 2020.
- A Comparison of Rule-Based and Machine Learning Methods for Classification of Spikes in EEG, W. Ganglberger, G. Gritsch, M. Hartmann, F. Fürbass, H. Perko, A. Skupch, T. Kluge, 2ND Internation Conference on medical information and Bioengineering 2017.
- Automatic spike detection with patient specific templates, M. Weinkopf, H. Perko, M. Hartmann, G. Gritsch, T. Kluge, American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting 2013.
[6] EEG monitoring in the intensive care
- Automated Long-Term EEG Review: Fast and Precise Analysis in Critical Care Patients. Koren J.P., Herta J., Fürbass F., Pirker S., Reiner-Deitemyer V., Riederer F., Flechsenhar J., Hartmann M., Kluge T., Baumgartner C., Front Neurol. June 2018.
- Reduced electrode arrays for the automated detection of rhythmic and periodic patterns in the intensive care unit: Frequently tried, frequently failed?, J. Herta, J. Koren, F. Fürbass, M. Hartmann , C. Baumgartner, A. Gruber, Clinical Neurophysiology, August 2017.
- Applicability of NeuroTrend as a bedside monitor in the neuro ICU, J. Herta, J. Koren, F. Fürbass, A. Zöchmeister, M. Hartmann , A. Hosmann, C. Baumgartner, A. Gruber, Clinical Neurophysiology, June 2017.
- Monitoring burst suppression in critically ill patients: Multi-centric evaluation of a novel method, F. Fürbass, J. Herta, J. Koren, M. B. Westover, M. Hartmann, A. Gruber, C. Baumgartner, T. Kluge, Clinical Neurophysiology, April 2016.
- Rhythmic and periodic EEG patterns of ‘ictal–interictal uncertainty’ in critically ill neurological patients, J. Koren, J. Herta, S. Pirker, F. Fürbass, M. Hartmann, T. Kluge, C. Baumgartner, Clinical Neurophysiology, February 2016.
- Automatic detection of rhythmic and periodic patterns in critical care EEG based on American Clinical NeurophysiologySociety (ACNS) standardized terminology, F. Fürbass, M.M. Hartmann, J.J. Halford, J. Koren, J. Herta, A. Gruber, C. Baumgartner, T. Kluge, Clinical Neurophysiology, September 2015.
- Prediction of rhythmic and periodic EEG patterns and seizures on continuous EEG with early epileptiform discharges, J. Koren, J. Herta, S. Draschtak, G. Pötzl, S. Pirker, F. Fürbass, M. Hartmann, T. Kluge, and C. Baumgartner, Epilepsy & Behavior, May 2015.
- Prospective assessment and validation of rhythmic and periodic pattern detection in NeuroTrend: A new approach for screening continuous EEG in the intensive care unit, J. Herta, J. Koren, F. Fürbass, M. Hartmann, T. Kluge, C. Baumgartner, and A. Gruber, Epilepsy & Behavior, May 2015.


